When Gypsum Meets Fibers
Innovations in Composite Materials for the Construction Industry
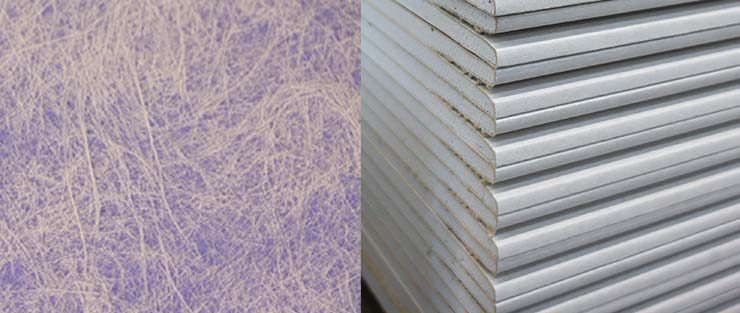
Gypsum-fiber composites are a type of construction material that combines gypsum with various fibers to enhance its properties.
The manufacturing process of gypsum-fiber composites typically involves mixing gypsum with water, fibers, and sometimes other additives like superplasticizers or mineral admixtures. The mixture is then cast into molds, compacted, and allowed to harden before being dried and trimmed to the desired shape.
Overall, gypsum-fiber composites represent a versatile and eco-friendly building material that combines the advantages of gypsum with the reinforcing properties of fibers, making them suitable for various construction applications such as walls, ceilings, and partitions.
Using gypsum composites benefits
Gypsum fiber composites offer several benefits as building materials in construction:
Improved mechanical properties: The addition of fibers, such as glass, hemp, or plant fibers, enhances the flexural, tensile, and compressive strength of gypsum composites compared to plain gypsum. This makes them more resistant to cracking and failure under loading.
Reduced density and thermal conductivity: Incorporating lightweight plant fibers like hemp or Alfa fibers into gypsum composites decreases the bulk density and thermal conductivity, improving thermal insulation performance. This can help reduce energy consumption in buildings.
Enhanced moisture regulation: Gypsum composites with plant fibers exhibit better moisture buffering capacity, helping to regulate indoor humidity levels and improve occupant comfort.
Sustainability: Gypsum composites promote sustainability by utilizing industrial by-products like coal fly ash as partial gypsum replacements, conserving natural resources. The low embodied energy of gypsum also contributes to their environmental benefits.
Lightweight and prefabrication: Fiber-reinforced gypsum composites can be designed as lightweight building materials suitable for prefabricated elements like partitions and panels. This enables faster and more efficient construction.
Versatility: Gypsum composites can be tailored by adjusting the type, length, and ratio of fibers to optimize their properties for specific applications, such as thermal and acoustic insulation.
Enhanced fire resistance: Gypsum is inherently fire-resistant, and when combined with fibers, it further improves the fire safety of the composite material.
Better thermal and acoustic insulation: The fiber reinforcement in gypsum composites contributes to improved thermal and acoustic insulation properties, making buildings more energy-efficient and comfortable.
Reduced brittleness: Gypsum is a brittle material, but the incorporation of fibers helps to mitigate this issue by distributing stresses more evenly throughout the matrix.
Potential for using waste materials: Some studies have explored the use of waste materials like date palm fibers or sheep wool fibers as reinforcement in gypsum composites, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
In summary, gypsum fiber composites offer a combination of improved mechanical performance, thermal and moisture regulation, sustainability, and versatility, making them attractive alternatives to traditional building materials in modern construction.
Cost of gypsum fiber composites compare to traditional construction materials
The key differences in cost between gypsum fiber composites and traditional construction materials are:
Material Costs: The incorporation of fibers, whether synthetic or natural, can increase the material costs of gypsum composites compared to traditional gypsum-based products. Synthetic fibers like glass fiber are generally more expensive than natural fibers like hemp or Alfa fibers.
Manufacturing Costs: The production process for gypsum fiber composites may be more complex and require specialized equipment, leading to higher manufacturing costs compared to simpler traditional gypsum materials.

Sustainability and Resource Conservation: While the use of industrial by-products and waste materials in gypsum composites can help reduce costs, the overall material costs may still be higher than traditional options. However, the long-term sustainability and resource conservation benefits of gypsum composites can offset the initial higher costs.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance: The improved thermal and acoustic insulation properties of gypsum fiber composites can lead to reduced energy costs and operational savings for buildings, potentially offsetting the higher initial material and manufacturing costs.
Versatility and Adaptability: The enhanced mechanical properties and design flexibility of gypsum fiber composites allow for a wider range of applications, which can provide cost advantages in certain construction scenarios compared to traditional materials.
In summary, while the initial material and manufacturing costs of gypsum fiber composites may be higher than traditional construction materials, the improved performance, sustainability, and versatility of these composites can potentially offset the higher upfront costs in the long run. The specific cost comparison will depend on the project requirements and the specific applications of the materials.

